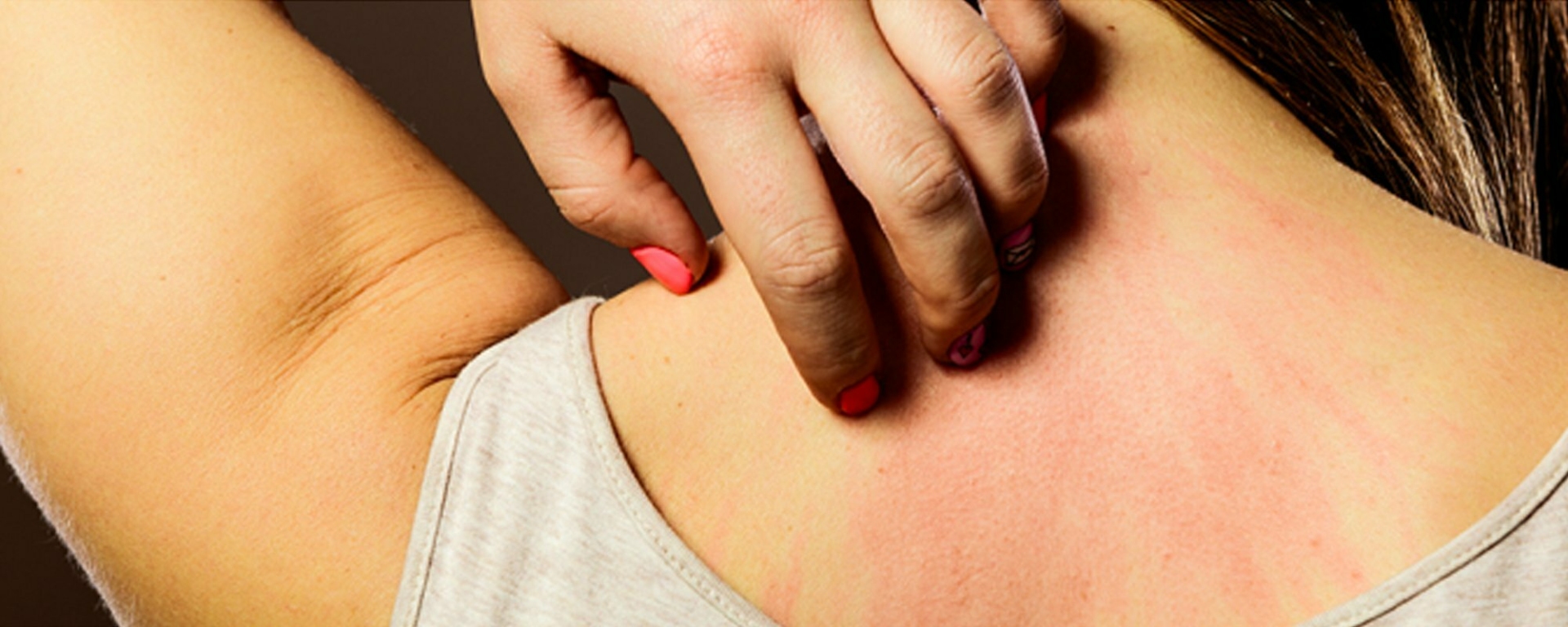
Hive symptoms
There are two main types of hives:
- Acute hives (lasting less than six weeks)
- Chronic hives (lasting more than six weeks)
Both types share the same key symptoms: red or pink raised welts, sometimes in clusters that itch intensely. The welts usually disappear within 24 hours without leaving scars.
Hive symptoms in men and women are generally the same, but men may sometimes delay seeking treatment, which can prolong discomfort.
If you experience other symptoms like fever, joint pain or night sweats, consult a doctor. Swelling of the throat, lips, or face is a medical emergency.
Hives causes
Identifying what causes hives can be tricky — 80% of cases have no clear cause. Common triggers include:
- Reactions to medications, foods, insect stings, animals, plants, pollen, cosmetics or chemicals
- Physical triggers like pressure, friction or exposure to cold or heat
- Emotional stress, which may worsen skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis
- Underlying conditions, such as autoimmune diseases or blood disorders
Stress and hives
Stress can disrupt your immune system and trigger hives. While not caused by allergens, stress-induced hives behave similarly and can be particularly frustrating for people with existing skin conditions.
This condition primarily affects young adults but can be especially bothersome for those already living with skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis. If you suspect your hives are triggered by stress, it’s best to consult with a pharmacist or doctor for proper guidance.
Allergies and hives
Many people associate hives with allergies — and rightly so. Allergic hives often appear soon after exposure to allergens like certain foods, medications or insect stings.
However, hives can also develop without an allergic reaction, for instance from infections, stress or exposure to cold. Identifying your triggers is essential to managing future outbreaks.
Hives treatment
There’s no instant cure for hives, but treatment can relieve symptoms.
For mild acute hives, symptoms often resolve on their own within a few hours. Taking over-the-counter antihistamines for several days can help reduce itching and swelling. For more severe or persistent cases, prescription treatments may be necessary — ask your Accès pharma pharmacist for advice.
To relieve the discomfort caused by itching, you can apply a topical cream to the affected area or take a bath with colloidal oatmeal. Don’t hesitate to ask your pharmacist for advice on the best ways to manage hive flare-ups.
Here are some additional tips to help reduce the intensity of your symptoms:
- Avoid scratching or irritating the affected area
- Wear loose, non-synthetic clothing
- Take cool showers or apply damp, cool compresses
If you experience severe swelling, especially of the face or throat, seek medical help immediately.
This information is not a substitute for professional medical advice and pharmacist-owners affiliated with Accès pharma cannot be held responsible for this information. The information was true and accurate at the time of publication, but it is subject to change.